Table of Contents
Advantages of Using SaaS
What is SaaS Management?
Contrasting Approaches: SMBs vs. Larger Enterprises
The Interrelation of SaaS Procurement and SaaS Management
Finding the Right Balance in Centralizing
The Decentralized SaaS Procurement & Centralized SaaS Management Model
Starting with SaaS Management: A Systematic Approach for Business Success
Key Takeaways
- SMBs and larger enterprises have contrasting approaches to SaaS management and SaaS procurement, with SMBs prioritizing affordability, agility, and self-service, while larger enterprises focus on centralization, strategic vendor relationships, integration, and compliance.
- Finding the right balance between centralized and decentralized approaches is crucial. A decentralized procurement and centralized management model can benefit SMBs by allowing both flexibility and control.
Advantages of Using SaaS Solutions
Using SaaS (Software as a Service) in a company offers several advantages and levels the playing field between small businesses and large enterprises. One significant benefit is cost-effectiveness, as SaaS tools for companies to eliminate the need for upfront investments in hardware, software licenses, and infrastructure. Instead, small organizations can subscribe to the required services and features, reducing IT expenses.
Software, surpassing staff costs, has emerged as the second most significant operative expenditure for companies. Despite an astounding 70-fold rise in spending on SaaS since 2015, this upward trend is expected to persist. Forrester predicts that by 2027, software will account for 42% of tech spending, up from 34% in 2022.
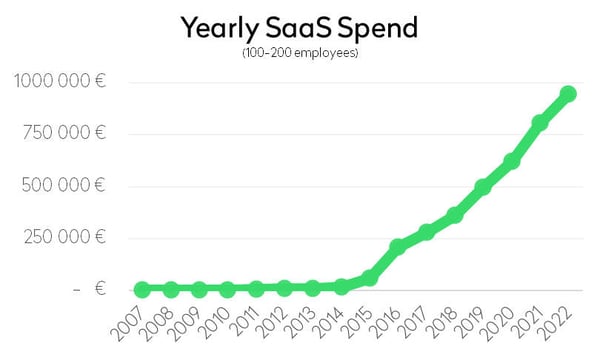
Scalability is another of the advantages of using SaaS. They provide flexible access to accommodate changing business needs for employees and decision-makers, allowing businesses of all sizes to quickly scale up or down their app usage without major infrastructure changes. This agility enables quick adaptation to evolving requirements.
SaaS also offers accessibility and convenience. Saas apps can be accessed from any location with an internet connection, making them suitable for remote work, distributed teams, and employees on the go. Users can access these apps through web browsers or mobile devices, promoting seamless collaboration and productivity across various devices and locations.
One notable benefit of SaaS is automatic updates and maintenance. Service providers take responsibility for software updates, security patches, and maintenance, ensuring that businesses benefit from regular updates and enhancements without disruptions to daily operations.
Integration and compatibility are also advantages of SaaS apps. The best SaaS products are designed to integrate with other systems and applications, facilitating data sharing and connectivity across different platforms. This interoperability enhances productivity and allows small businesses to leverage existing tools while expanding their capabilities.
SaaS apps provide enhanced security measures. Reputable providers employ encryption, regular backups, and stringent access controls to protect data. By relying on trusted SaaS apps, businesses benefit from advanced security features and expertise that are cost-prohibitive to implement in-house.
Streamlined collaboration is another advantage of SaaS apps. They offer real-time document editing, file sharing, and project management tools, promoting teamwork and efficient collaboration among employees, departments, and external stakeholders.
Using SaaS reduces the IT burden on small businesses and their employees. Companies can free up their IT teams (if they have any) to focus on strategic initiatives and core functions by relying on service providers for tasks like software installation, updates, and troubleshooting.
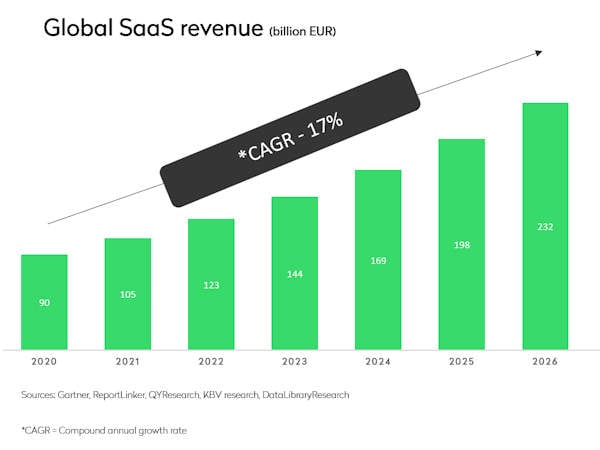
Medium-sized companies are propelling growth in 2023, witnessing a 35% surge in their utilization of SaaS apps compared to the previous year. Over the next three years, spending will experience an approximate 20% year-on-year increase.
However, larger enterprises, being pioneers in implementing enhanced processes and support systems for SaaS management, are leading the way toward app consolidation and stabilized spending patterns.
What is SaaS Management?
SaaS management refers to managing cloud-based applications, and the goal of SaaS management is to ensure they are used effectively and securely and comply with company policies. It involves several key components that work together to achieve these objectives.
.jpg?width=249&height=623&name=5%20risks%20with%20not%20managing%20the%20SaaS-portfolio%20(3).jpg) The first component is SaaS vendor and application discovery. This entails identifying and cataloging all the cloud-based applications used within the business, which can be challenging due to unauthorized applications and unmanaged tools.
The first component is SaaS vendor and application discovery. This entails identifying and cataloging all the cloud-based applications used within the business, which can be challenging due to unauthorized applications and unmanaged tools.
Once the inventory of cloud-based applications is established, the organization moves on to application rationalization. This step involves assessing the necessity of each application and determining whether any can be eliminated or consolidated, streamlining the SaaS portfolio.
After identifying the necessary applications, the focus shifts to application adoption. The organization ensures these applications are used effectively among employees by providing IT management training and support to maximize user productivity and effectiveness.
SaaS security is another crucial aspect of SaaS management. Cloud-based applications can introduce security risks, especially if they handle sensitive data. Managing the tech stack involves implementing robust security measures, such as access controls and encryption, to protect data and minimize potential vulnerabilities.
Additionally, compliance management is essential to SaaS management, particularly for industries subject to stringent data privacy and security regulations. This component ensures that all applications used comply with relevant regulations. Compliance work includes SaaS license management and ensuring the proper deployment of SaaS among employees aligns with regulatory requirements.
By addressing these key components, organizations can effectively manage their SaaS apps, optimizing their usage, maintaining security, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Contrasting Approaches to SaaS Management and Procurement: SMBs vs. Larger Enterprises
Due to organizational size, resources, and complexity, SMBs (small and medium-sized businesses) and larger enterprises have different SaaS management and procurement approaches. Here are some key differences in their approaches.
SMBs' Approach to SaaS Management and Procurement
SMBs have leaner organizational structures and fewer decision-making layers. They simplify their SaaS management and procurement processes for quicker decision-making and implementation. SMBs often have more streamlined approval cycles and fewer stakeholders involved in the decision-making process.
Cost considerations are crucial for SMBs. Business leaders in small businesses prioritize affordable SaaS solutions and seek value for money. They focus more on cost-effectiveness, exploring discounts and opting for flexible pricing models (e.g., monthly subscriptions) to manage costs within their limited budgets.
SMBs leverage their agility to adopt and experiment with new SaaS tools for businesses quickly. They may be more willing to take risks and try different solutions without going through extensive procurement processes. This flexibility allows them to rapidly adapt to changing business needs and market dynamics.
SMBs may rely on self-service models and emphasize user empowerment in SaaS management. They may encourage individual departments or teams to select and manage their SaaS based on specific needs and workflows. This approach allows SMBs to distribute responsibilities and reduce the burden on central IT teams.
Larger Enterprises' Approach to SaaS Management and Procurement
Larger enterprises have more complex organizational structures. They tend to centralize SaaS management and procurement under a governance framework. This centralized approach enables standardization, more automation of administrative tasks, and enforcement of policies and security measures across the organization.
They often establish strategic relationships with key SaaS vendors and focus on consolidating procurement with select vendors to negotiate favorable terms, obtain volume discounts, and access specialized support and services. Strategic vendor management allows larger companies to leverage their scale and purchasing power.
The diverse IT landscape with multiple systems and applications makes larger enterprises prioritize SaaS that integrates with their existing infrastructure and automates workflows. Integration capabilities, compatibility with existing systems, for example, Enterprise Resource Planning system (ERP), and interoperability become critical factors in their SaaS management and procurement decisions.
Larger enterprises have more standardized SaaS management and procurement processes. They establish robust workflows, documentation, and compliance frameworks to ensure adherence to internal policies, industry regulations, and security standards.
They also invest more heavily in procurement analytics and performance metrics to assess the effectiveness of their SaaS procurement for different business functions. They require SaaS that meets their enterprise-level needs. Support for multi-tenancy and enterprise-grade features are vital considerations.
The Interrelation of SaaS Procurement and SaaS Management
Before deciding on a SaaS management strategy, it is crucial to determine whether a centralized or decentralized approach to SaaS procurement suits the company's structure and needs. Ultimately, finding the right balance between centralization and decentralization depends on organizational structure, culture, resource availability, and the desired level of control and agility.
While centralizing SaaS procurement has several advantages, there are also considerations and potential drawbacks that businesses should consider. Allowing departments to buy and manage their SaaS applications increases ownership and alignment with department needs. Still, without clear policies and a common overview, it often leads to duplicate applications, lack of visibility, and compliance & security risks.
Finding the Right Balance in Centralizing
Finding the right balance involves considering various factors. For SMBs, it is essential to evaluate the appropriateness of centralization based on the following considerations:
One crucial consideration is specialized department needs. Different departments or teams within an organization often have unique requirements for SaaS apps based on their specific functions and workflows. Centralizing procurement may not provide the flexibility to cater to these specialized needs. In such cases, decentralized procurement allows individual departments to choose and manage SaaS applications that best suit their requirements.
Another aspect to consider is the speed of adoption and experimentation. Decentralized procurement empowers departments or teams to swiftly adopt and experiment with new SaaS tools without undergoing a lengthy and centralized procurement process. This agility is especially valuable in fast-paced environments where rapid innovation and experimentation play a vital role.
Budget allocation is another factor to weigh. Centralized procurement often means that budgets for SaaS are managed centrally. However, in some organizations, departments or teams may have separate budgets and financial autonomy. Decentralized procurement allows them to retain control over their budgets and make purchasing decisions accordingly.
Vendor relationships and negotiations also come into play. Decentralized procurement enables individual departments or teams to establish direct relationships with SaaS vendors. This provides them with better leverage for negotiations and allows for personalized support tailored to their needs. It fosters collaboration and the potential for beneficial vendor partnerships.
Lastly, streamlined decision-making is an advantage of decentralized procurement. In centralized procurement, decision-making for SaaS applications typically involves more stakeholders and a lengthier process. On the other hand, decentralized procurement empowers individual departments or teams to make purchasing decisions, reducing bureaucratic hurdles and streamlining the decision-making process.
The Decentralized SaaS Procurement & Centralized SaaS Management Model
Many SMBs strive to adopt a hybrid approach where some critical or company-wide SaaS tools are centralized while allowing flexibility for decentralized procurement and management in other areas. A decentralized SaaS procurement and centralized SaaS management strategy are beneficial for most SMBs.
By leveraging the advantages of decentralized procurement and centralized management, organizations can balance user autonomy and organizational control, leading to effective SaaS implementation, cost optimization, and streamlined operations..jpg?width=720&height=405&name=The%20Decentralized%20SaaS%20Procurement%20%26%20Centralized%20SaaS%20Management%20model%20(1).jpg)
Benefits of decentralized SaaS procurement
Decentralized procurement allows individual teams or departments to choose SaaS solutions that best fit their needs. Different teams have unique requirements and domain-specific expertise. Decentralized procurement empowers teams to select SaaS that aligns with their specific workflows and industry needs. With decentralized procurement, teams can independently evaluate and choose SaaS apps without going through a centralized decision-making process. This expedites the procurement process and avoids potential bottlenecks. This flexible access can lead to better adoption and satisfaction among users.
Benefits of Centralized SaaS Management
Centralized management allows for bulk purchasing of SaaS licenses, resulting in cost savings and improved budget control. It enables consistent deployment, configuration, and usage of SaaS across the organization. It promotes standardization of processes, business intelligence and data management, and security practices, which enhance efficiency and minimize risks. Centralized control ensures adherence to organizational policies, security protocols, and regulatory requirements. It enables centralized monitoring and reporting, which is essential for data protection and compliance.
Considerations for Success
Effective communication channels and collaboration mechanisms should be established. This ensures alignment, knowledge sharing, and business intelligence insights regarding SaaS solutions.
Clearly defined policies and guidelines should be in place to provide boundaries and frameworks for both procurement and management processes. These should outline criteria for solution selection, budget considerations, security requirements, and compliance obligations.
Regular feedback loops should be established to gather end-user input and assess the performance of selected SaaS solutions. This information can inform future procurement decisions and optimize the centralized management approach.
Starting with SaaS Management: A Systematic Approach for Business Success
When approaching SaaS management, companies should follow a systematic approach to ensure that the result aligns with business objectives, maximizes efficiency, and delivers value to the organization. Here are suggestions on steps to take:
Assess business needs & define a strategy
Develop a clear understanding of the company's requirements and pain points and define a SaaS management and procurement strategy that aligns with the organization's goals and resources. Consider factors such as budget, scalability, security, and compliance requirements. Determine whether a centralized, decentralized, or hybrid approach suits the organization's structure and needs.
Conduct research on SaaS solutions
Explore the market to identify suitable SaaS management platforms aligned with the defined strategy. Consider factors such as functionality, ease of use, integration capabilities, vendor reputation, and pricing. Research online reviews, seek recommendations from trusted sources, and evaluate vendor websites.
Engage stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders in decision-making, such as department heads and billing owners. Gather their input and understand their specific needs and preferences. This collaborative approach ensures that the selected SaaS management platform meets the requirements of different teams within the organization.
Evaluate security and compliance
When selecting a SaaS management platform, consider security and compliance requirements. Ensure the chosen SaaS management tool aligns with industry regulations and internal security standards and assess the vendor's data security measures and privacy policies.
Pilot and test
Before committing to a long-term contract, consider piloting the selected SaaS management platform with a small group or on a trial basis. This allows you to evaluate the functionality, user experience, and compatibility with existing systems. Solicit feedback and assess whether the SaaS management platform meets expectations and delivers the desired outcome.
Implement and train
Once the SaaS management platform is selected, allocate resources for implementation and deployment. Train users on effectively utilizing the chosen applications, ensuring they understand the value and perks of using the SaaS solution.
If you work in a small or medium-sized business and seek a SaaS management platform with a short learning curve that is user-friendly and strengthens the cooperation between IT and Business, consider exploring Substly to see if it suits your needs.
.jpg)


